Gas regulators are an important component in welding, but many welders may not fully understand what they are or how they work. In this article, we’ll introduce you to the basics of gas regulators and explain why they’re critical for safe and effective welding.
Simply put, a gas regulator is a device that controls the flow and pressure of gases used in welding, such as oxygen, acetylene, or argon. This is important because different welding applications require different levels of gas flow and pressure. Without a gas regulator, you would have little control over the amount of gas that is being used in your welding, which could lead to unsafe or ineffective results.
At their most basic level, gas regulators work by taking high-pressure gas from a cylinder and reducing it to a lower, more consistent pressure for use in welding. This is accomplished through a series of valves and diaphragms that regulate gas flow and pressure. There are several types of gas regulators available, each with their own strengths and weaknesses.
While gas regulators may seem like a technical and complex topic, understanding the basics is important for safe and effective welding. In the following sections, we’ll break down how gas regulators work, the different types available, how to select the right one for your needs, and best practices for installation and maintenance.
In this guide:
Huge Savings on Regulators!
We offer a wide range of Gas Regulators that are designed for use in various applications and industries.
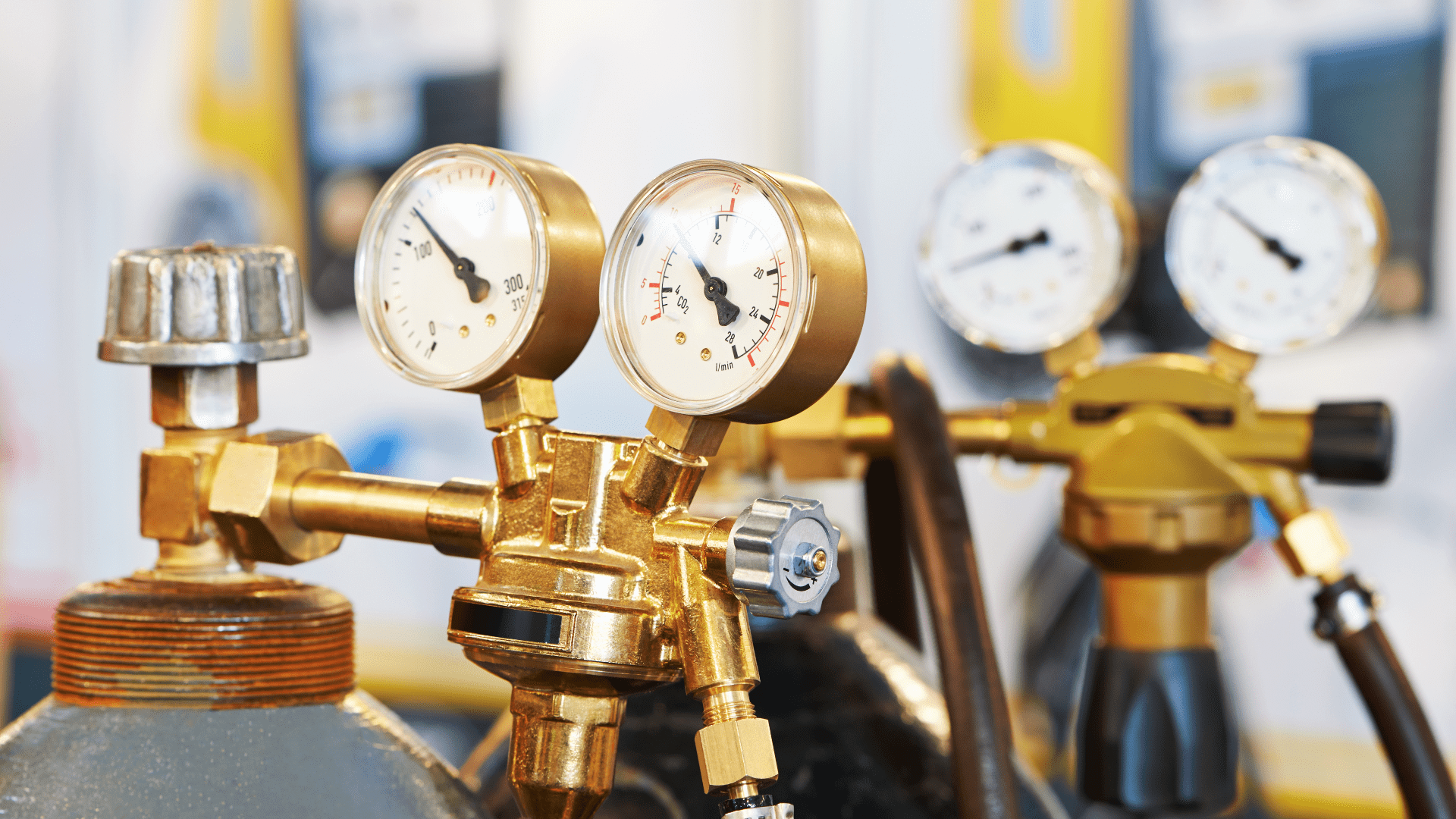
How gas regulators work
To better understand gas regulators, it’s important to first understand the principles of pressure and flow control in welding. In welding, gases such as oxygen, acetylene, or argon are used to create the heat and shielding necessary to melt and fuse metals together. However, the amount of gas needed for a given application can vary widely depending on factors such as the size of the weld, the type of metal being welded, and the desired finish.
This is where gas regulators come in. A gas regulator is designed to take high-pressure gas from a cylinder and reduce it to a lower, more consistent pressure for use in welding. Gas regulators work by using a series of valves and diaphragms to regulate gas flow and pressure. Here’s how it works:
- Gas enters the regulator through the inlet port, which is connected to a high-pressure gas cylinder.
- The gas then travels through a filter and into the main valve assembly, where it is regulated by a diaphragm and spring mechanism.
- The diaphragm and spring work together to control the pressure of the gas as it flows out of the regulator.
- As gas is used in the welding process, the pressure inside the regulator decreases. This causes the diaphragm to flex, which opens the valve and allows more gas to flow in from the cylinder, maintaining a consistent pressure.
It’s important to note that gas regulators can be affected by factors such as temperature, humidity, and gas purity. For example, changes in temperature can cause the pressure of the gas to fluctuate, which can impact the consistency of the weld. Similarly, impurities in the gas can cause the regulator to malfunction, leading to unsafe or ineffective welding.
Understanding how gas regulators work is essential for selecting the right type of regulator for your welding needs, as well as for maintaining and troubleshooting your regulator for optimal performance.
Types of gas regulators
There are several types of gas regulators available, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. The most common types of gas regulators used in welding include single-stage, dual-stage, high-pressure, low-pressure, and specialty regulators. Here’s a brief overview of each type:
Single-stage gas regulators: These regulators are designed to reduce the pressure of gas in a single step. They are commonly used for applications that require relatively constant pressure, such as cutting or brazing.
Dual-stage gas regulators: These regulators are similar to single-stage regulators, but they reduce the pressure of gas in two steps instead of one. This makes them better suited for applications that require a more precise and stable pressure, such as TIG welding.
High-pressure gas regulators: These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure gases, such as those used in oxy-fuel welding. They are built with heavy-duty components to withstand the higher pressures and flows required for these applications.
Low-pressure gas regulators: These regulators are designed to handle lower-pressure gases, such as those used in MIG or TIG welding. They are typically more precise and sensitive than high-pressure regulators, and are better suited for applications that require fine control over gas flow and pressure.
Specialty gas regulators: These regulators are designed for specific applications, such as those that require the use of exotic or highly reactive gases. They may have unique features or components that are not found in standard gas regulators.
When selecting a gas regulator, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your welding application. Factors to consider include the type of gas being used, the desired pressure and flow rate, and the type of welding being performed. It’s also important to ensure that the regulator is compatible with your welding equipment and that it meets safety standards.
Selecting the right gas regulator
Selecting the right gas regulator for your welding needs is critical for achieving optimal performance and safety. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a gas regulator:
Gas type: The type of gas being used in your welding application will dictate which gas regulator you need. Different gases have different pressure and flow requirements, so it’s important to choose a regulator that is compatible with the specific gas you will be using.
Application: The type of welding application you will be performing will also impact your choice of gas regulator. For example, if you are doing TIG welding, you will likely need a dual-stage regulator that can provide precise control over gas flow and pressure. On the other hand, if you are doing oxy-fuel welding, you will need a high-pressure regulator that can handle the higher pressure and flow rates required for that application.
Gas flow rate: The flow rate of gas needed for your welding application will also impact your choice of gas regulator. Higher flow rates will require a regulator that can handle greater volumes of gas, while lower flow rates may require a regulator with greater sensitivity and precision.
Equipment compatibility: It’s important to ensure that the gas regulator you choose is compatible with your welding equipment. This includes the type of welding torch, hoses, and fittings you are using. Some gas regulators may require special adapters or fittings to work with specific equipment.
Safety standards: Finally, it’s important to choose a gas regulator that meets safety standards and regulations. Look for regulators that are certified by organizations such as the American Welding Society (AWS) or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
When selecting a gas regulator, it’s also important to consider the brand and quality of the regulator. Choose a reputable brand, such as Gas Arc regulators, that has a proven track record of quality and reliability. Additionally, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation and use, and perform regular maintenance and inspections to ensure optimal performance.
The table below shows the most common gas regulator types and their suitable welding applications:
| Regulator Type | Suitable Welding Applications |
| Single-stage | Cutting, brazing |
| Dual-stage | TIG, MIG |
| High-pressure | Oxy-fuel welding |
| Low-pressure | MIG, TIG |
| Specialty | Exotic or highly reactive gases, specialized applications |
Installing and maintaining gas regulators
Proper installation and maintenance of your gas regulator is critical for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Here are some best practices for installing and maintaining your gas regulator:
Installation: When installing your gas regulator, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. This includes properly connecting the regulator to the gas cylinder, ensuring that all hoses and fittings are tight and secure, and properly adjusting the regulator to the correct pressure and flow rate. Be sure to also wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and work in a well-ventilated area.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your gas regulator functioning properly. This includes performing routine inspections to check for leaks or damage, cleaning the regulator as needed, and replacing worn or damaged components. Be sure to also replace the regulator’s diaphragm and springs at regular intervals, as these can wear out over time.
Troubleshooting: If you encounter problems with your gas regulator, it’s important to troubleshoot the issue as soon as possible. Common issues include leaks, inconsistent gas flow, and incorrect pressure. Be sure to consult the manufacturer’s instructions and seek professional assistance if needed.
Safety considerations: When handling and using gas regulators, it’s important to follow safety guidelines to minimize the risk of injury or damage. This includes wearing appropriate PPE, storing gas cylinders properly, and avoiding exposure to gas leaks or spills. Be sure to also properly dispose of used gas cylinders and components according to local regulations.
By following these best practices for installing and maintaining your gas regulator, you can ensure optimal performance and safety in your welding work. It’s also important to stay up-to-date on the latest safety guidelines and regulations, and to seek professional assistance if you have any questions or concerns about your gas regulator.
Final Thoughts
Gas regulators are a critical component in welding, allowing you to control the flow and pressure of gases for safe and effective welding. By understanding the basics of how gas regulators work, the different types available, and how to select, install, and maintain them properly, you can ensure optimal performance and safety in your welding work.
Remember that different welding applications require different types of gas regulators, so it’s important to choose a regulator that is specifically designed for your needs. When selecting a gas regulator, consider factors such as the type of gas being used, the desired flow rate and pressure, and the compatibility with your welding equipment.
Proper installation and maintenance of your gas regulator is also critical for optimal performance and safety. Regular maintenance and inspections, as well as troubleshooting any issues that arise, can help prevent unsafe or ineffective welding.
By following best practices and dispelling common myths and misconceptions about gas regulators in welding, you can be confident in your ability to select, install, and maintain your gas regulator for safe and effective welding work.
We hope this article has provided you with a solid introduction to gas regulators in welding. If you have any further questions or concerns about gas regulators or welding equipment, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance.